For industrial plants, electrical service is often provided at 208 volts. That voltage can be supplied as a single phase or three-phase power. Each of these options has its own benefits and drawbacks, so it’s important to understand how they work and what factors should be considered when choosing the right one for your needs. The primary benefit of 208 volt vs 220 volt is the lesser current (amperage). At 208 volts, the load on an individual circuit or device will be less stressful and therefore have a longer life expectancy. Also, 208 volt service may qualify for incentives in some locations where utilities are encouraging customers to adopt more energy-efficient services; generally speaking, lighting loads at 208 volts use less energy than the same loads at 220 volts.
What is 208-volt single-phase power?
208-volt single-phase power is used in many industrial and commercial applications. It’s most commonly used to provide service to lighting loads, but it can also be used to supply power to other types of equipment such as motors, transformers, and switch gear. A 208 volt single-phase service consists of a two-wire, 120/240-volt, single-phase circuit with a 208 volt source. A 208 volt single-phase circuit is typically fed through a single-phase, three-wire circuit breaker and fed to a 208-volt panel board where it is then distributed to the 208 volt loads. A 208-volt panel board is designed and built to supply 208 volt power to the 208 volt loads, and it is also designed to bring the voltage up to a suitable voltage for feeding it to other loads that are designed to be fed from 120 volt power.
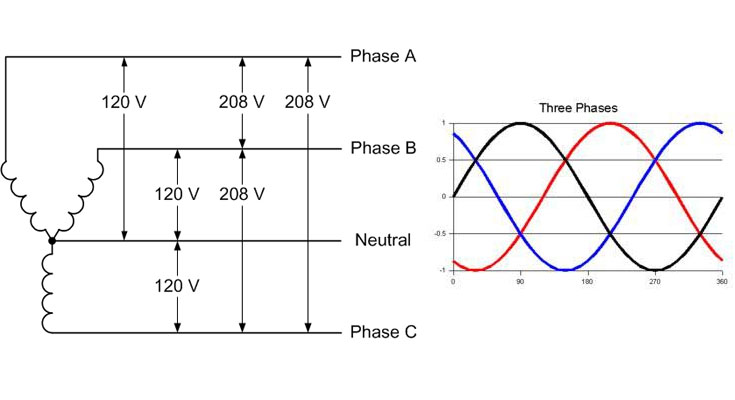
What is 208-volt 3-phase power?
208 volt 3-phase power is three single-phase circuits fed from a single 208 volt source. In a 208 volt 3-phase service, each of the three single-phase circuits is fed from one of three sources of 208 volt power, and each of those three sources is out of phase with the other two sources by 120 degrees. The 208 volt 3-phase service is typically fed through a three-phase, three-wire circuit breaker and fed to a 208 volt panel board where it is then distributed to the three single-phase loads. A 208 volt 3-phase panel board is designed and built to supply 208 volt power to the 208 volt loads, and it is also designed to bring the voltage up to a suitable voltage for feeding it to other loads that are designed to be fed from 120 volt power.
What are the benefits of 208 volt 3 phase power?
The primary benefit of 208 volt 3-phase power is that it is more efficient than 208 volt single-phase power. At 208 volts, the load on an individual circuit or device will be less stressful and therefore have a longer life expectancy. Also, 208 volt 3-phase power can be fed to loads that are designed to be fed from 208 volt single-phase service. A 208 volt 3-phase service is fed to a panel board that is designed to supply 208 volt power to the 208 volt loads and is also designed to bring the voltage up to a suitable voltage for feeding it to other loads that are designed to be fed from 120 volt power.
Drawbacks of using 208 volt 3 phase service?
The primary drawback of 208 volt 3-phase power is that it is more expensive than 208 volt single-phase power. A 208 volt 3-phase service is fed to a panel board that is designed to supply 208 volt power to the 208 volt loads and is also designed to bring the voltage up to a suitable voltage for feeding it to other loads that are designed to be fed from 120 volt power.