Matthew Roskoff Delves into Private Client Portfolio Engineering
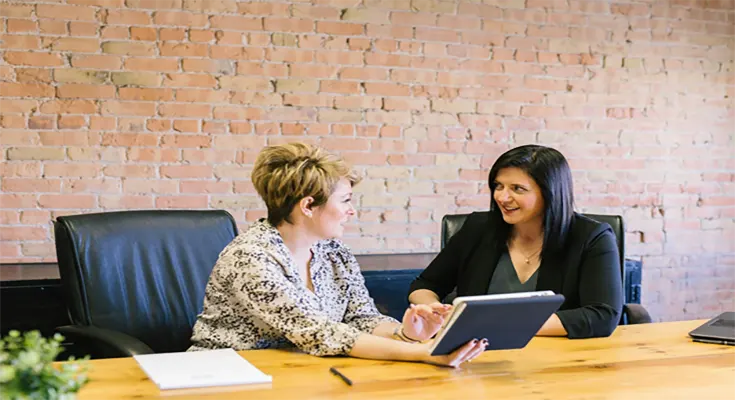
Private client portfolio engineering offers a highly tailored approach to managing wealth, focusing on the unique needs and aspirations of high-net-worth individuals. Combining advanced tools, personalization, and long-term strategies ensures that financial goals are met efficiently while addressing complex challenges like tax efficiency, market volatility, and generational wealth transfer.
Matthew Roskoff notes how this process emphasizes not just achieving financial success but aligning investments with personal values, lifestyle, and life stages. By utilizing diversification, risk management, and cutting-edge techniques, portfolios are optimized to provide growth and stability. Moreover, the dynamic nature of these strategies ensures they adapt seamlessly to changing market conditions or major life events.
Private Client Portfolio Engineering
Private client portfolio engineering is a specialized approach to managing investments for high-net-worth individuals. It focuses on designing personalized strategies that align with unique financial goals, risk preferences, and long-term aspirations. Unlike general portfolio management, which often applies broad strategies, …
Matthew Roskoff Delves into Private Client Portfolio Engineering Read More